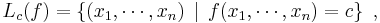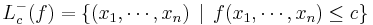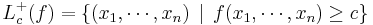Level set
For the computational technique, see Level set method.
For level surfaces of force fields, see equipotential surface.
In mathematics, a level set of a real-valued function f of n variables is a set of the form
that is, a set where the function takes on a given constant value c.
When the number of variables is two, a level set is generically a curve, called a level curve, contour line, or isoline. When n = 3, a level set is called a level surface (see also isosurface), and for higher values of n the level set is a level hypersurface.
A set of the form
is called a sublevel set of f (or, alternatively, a lower level set or trench of f).
is called a superlevel set of f.[1][2]
A level set is a special case of a fiber.
Properties
- The gradient of f at a point is perpendicular to the level set of f at that point.
- The sublevel sets of a convex function are convex (the converse is however not generally true).
See also
References
- ^ Voitsekhovskii, M.I. (2001), "Level set", in Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1556080104, http://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=L/l058220
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W., "Level Set" from MathWorld.